Aliphatic diisocyanates (ADI) are specialty intermediate chemicals used primarily to make durable coatings, adhesives, sealants, elastomers, and
textiles, among other products. Generally, they are considered to be specialty materials used in significantly smaller quantities than the aromatic diisocyanates.
- In total, ADIs represented less than five percent of overall isocyanate consumption in the North American polyurethane industry.1
- ADIs are typically not sold directly for consumer use. Rather, they are sold primarily to industrial customers who use them as binders or hardeners during manufacturing processes.
ADIs are often reacted to form polyisocyanates, which act as building blocks to form color-stable and durable polyurethane coatings, sealants, adhesives and elastomers. These coatings and elastomers can significantly enhance a product’s appearance, lengthen its lifespan and offer high abrasion and UV resistance.
How Are Aliphatic Diisocyanates Used?
Aliphatic diisocyanates are primarily used to make resins used in paint and surface coatings applied in the
adhesive,
automotive,
marine and
aircraft industries. Coatings prepared with ADIs can have excellent resistance to chemicals and abrasion. They also demonstrate superior weather resistant characteristics, including gloss retention and resistance to yellowing and chalking.
- For example, durable coatings made with ADIs can protect military, commercial and passenger vehicles from UV damage. They are often used in military vehicles or infrastructure (i.e. bridges) applications to combat harsh conditions.
- ADIs also can be reacted with other resins to form polymers (containing no residual isocyanate) dispersed in water or solvent that can be used in Do-it-Yourself (DIY) products such as clear wood finishes.2, 3
ADIs are also used to make urethane-based polymers which are formulated into heat-activated or contact adhesives. Benefits include improved heat and moisture resistance, as well as providing greater adhesion on oily substrates.
- Typical uses include adhering wood on wood, PVC lamination on wood, automotive, footwear and construction applications.
They are also used in construction sealants. ADIs help improve durability, weather resistance and stability in exterior applications. Smaller amounts are used in specialty applications such as leather refinishing, textile and fiber treatments, ink, thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) sheets and others to provide UV protection and durability.3
Types of Aliphatic Diisocyanates
The most common types of aliphatic diisocyanates include:
- hexamethylene diisocyanate (HDI)
- methylene dicyclohexyl diisocyanate or hydrogenated MDI (HMDI)
- isophorone diisocyanate (IPDI)
These raw materials come in two main forms:
- Monomeric Diisocyanates – HDI, IPDI and HMDI (and several others)
- Blocked Polyisocyanates – (mainly based on HDI)
Blocked Polyisocyanates are supplied as 100% solids and/or dissolved in a variety of solvents.
Polyisocyanates are either based on HDI or IPDI. The most common products include:1
- HDI trimer
- HDI biuret
- HDI uretdione
- IPDI trimer
They are typically available as 100% solids or dissolved in a variety of solvents.
HDI:
The most widely used ADI is hexamethylene-1,6-diisocyanate (HDI).1 It is derived from hexamethylene diamine. HDI is an intermediate chemical used to produce HDI-based products (i.e. polyisocyanates). These HDI-based products are primarily used in the manufacture of industrial coatings where high performance capability (e.g. UV and weather resistance) is required. HDI-based coatings are used in the manufacture a variety of products, including automobiles, aircraft, flooring, furniture, safety equipment, machinery, medical devices and infrastructure projects.
HMDI:
Dicyclohexylmethane-4,4’diisocyanate (HMDI) serves as a building block for the preparation of chemical products, reactive intermediates and polymers such as polyurethane dispersions (PUDs), elastomers, and thermoplastic polyurethanes (TPUs). Products based on HMDI may be useful in coatings for flooring, roofing, textiles, elastomers, optical products, adhesives, and sealants.
IPDI:
Isophorone diisocyanate (IPDI) is an intermediate chemical used to produce IPDI-based products (i.e., polyisocyanates, polyurethane dispersions) that are primarily used in certain polyurethane coatings. These IPDI-based products are used by industrial customers to manufacture various coatings for automobiles, flooring, roofing, machinery, and textile applications. They are also used in cast elastomers, adhesives, sealants, and as crosslinkers for powder coatings.
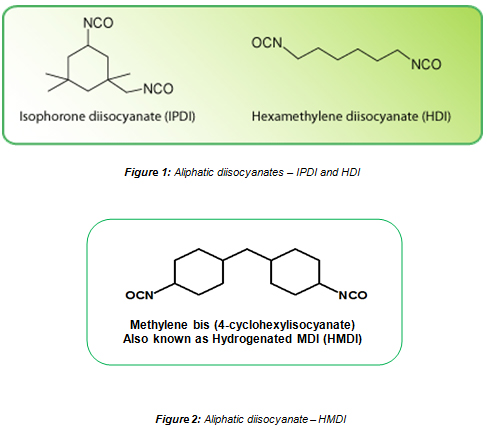
Aliphatic Diisocyanates:
Shown below is the chemical composition of several key aliphatic diisocyanates: IPDI, HDI and HMDI.
Chemical Composition of the Aliphatic Diisocyanates: IPDI, HDI and HMDI
Aromatic Diisocyanates
There are two primary aromatic diisocyanates:
toluene diisocyanate (TDI) and
methylenediphenyl diisocyanate (MDI). TDI is used primarily in the production of flexible foams. MDI, the second type of aromatic, comes in two forms: Pure MDI and polymeric MDI (PMDI). Pure MDI is used in the production of a variety of polyurethane products like elastomers, sealants, adhesives and coatings. PMDI is a highly versatile product used to produce a wide variety of rigid, flexible, semi-rigid and polyisocyanurate and thermoset foams.
Visit the ACC
diisocyanates website for more information about aromatic diisocyanates.
1 ACC Center for the Polyurethanes Industry 2014 End-Use Market Survey
2 Polyurethanes, Coatings, Adhesives and Sealants, Ulrich Meier-Westhues, Hannover: Vincentz Network, 2007, pp. 52-55.
3 “Wood Floor Coating Technology Comparison,” Bayer MaterialScience publication #20937, Bayer MaterialScience LLC, 2012.